Despite Saudi Arabia coming under intensified international scrutiny after last year’s brutal murder of journalist Jamal Khashoggi inside the Saudi consulate in Istanbul, a new study shows Riyadh has been on a record-setting weapons buying spree over the past two years.
And who supplies most of these arms? Of course the United States, which has by all indicators done nothing to curtail its perpetual arms pipeline to the Saudis; instead it has grown. According to a new 2019 study published in March from arms transfer monitoring group, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), 70 percent of the Saudi arsenal now comes from the United States.

Prior file photo of Saudi officers take photos during a joint military exercise of 21 Muslim nations (in 2016). Image source: Getty
Furthermore, the Saudis have hands down led the world in global weapons purchases for the past two years, and there’s little sign this trend will let up as Riyadh keeps up its merciless bombing campaign over neighboring Yemen, and as its regional ambitions have grown in competition with perceived “Iranian influence” — also given Syria’s Assad emerging victorious in the long-running proxy war in Syria, and as Hezbollah is now considered stronger than ever.
Senior researcher and Middle East specialist with SIPRI, Pieter Wezeman, told PRI the US-Saudi arms trade has continued to grow: “There’s been a very significant growth in arms supplies to Saudi Arabia by the US,” he said.
He detailed the bulk constitutes major weapons systems as follows:
To Saudi Arabia, the US supplies a very wide range of arms. The most important types of arms include combat aircraft, tanks and missiles. It includes very advanced sensors and intelligence gathering equipment, often on planes. In the coming years, it will also include frigates and other ships. So, really, the whole package of weapons which Saudi Arabia wants to have is what the US is willing to supply and already has supplied.
Wezeman also suggested the Saudis are worried about Iranian escalation in Yemen. Saudi officials have long accused Tehran of transferring ballistic missiles to Shia Houthi rebels, in order to strike at targets deep inside Saudi Arabia.
“What would have happened if one of those ballistic missiles would have killed many hundreds or if it would have killed a high-level royal family member?” Wezeman mused in his comments to PRI, reflecting Saudi fears.
He explained further that Saudi motives for its arms buying rampage of the past years remain largely concealed, leaving analysts to speculate on the more obvious geopolitical factors: “We don’t have a nice Saudi Arabian defense whitepaper which clearly explains why they want to have all these arms,” he said. “We have to look at how they behave, statements made here and there by important Saudi Arabian people, in particular, the crown prince.”
Wezeman added: “And it is quite clear that the prime motive of motives for Saudi Arabia are that it wants to be a regional power and that weapons are considered an important tool for becoming that, and that it sees Iran as an important competitor in that struggle for regional power.”
Elsewhere the SIPRI study reported that the United States remains by far the world’s undisputed lead weapons supplier, growing exports by 29% between 2009–2013 and 2014–2018. The report found and the US share of total global exports went from 30% to 36% during the same period of comparison.
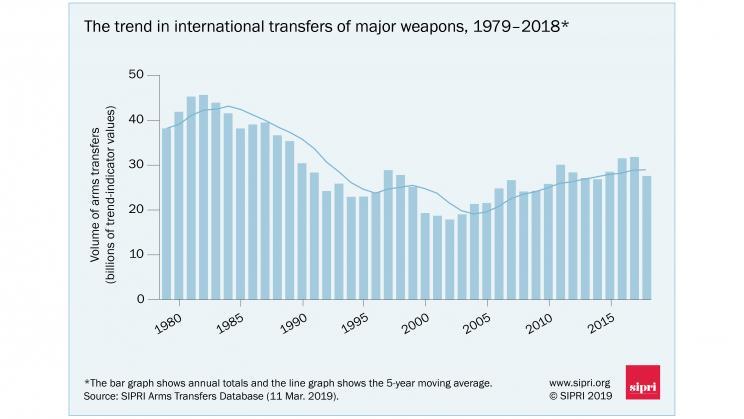
Via SIPRI: The trend in international transfers of major weapons, 1979—2018.
More significant is the degree to which the United States is far outpacing Russia in the midst of what some observers have lately dubbed the “new Cold War”.
According to the report:
The gap between the top two arms-exporting states also increased: US exports of major arms were 75 per cent higher than Russia’s in 2014–18, while they were only 12 per cent higher in 2009–13. More than half (52 per cent) of US arms exports went to the Middle East in 2014–18.‘The USA has further solidified its position as the world’s leading arms supplier,’ says Dr Aude Fleurant, Director of the SIPRI Arms and Military Expenditure Programme. ‘The USA exported arms to at least 98 countries in the past five years; these deliveries often included advanced weapons such as combat aircraft, short-range cruise and ballistic missiles, and large numbers of guided bombs.’
One interesting data point regarding Russia’s lagging behind in global arms sales relates to Venezuela and India: “Arms exports by Russia decreased by 17 per cent between 2009–13 and 2014–18, in particular due to the reduction in arms imports by India and Venezuela,” the report noted.

Meanwhile US Congress has lately signaled it would try to put greater distance between Washington and Riyadh military cooperation, along with seeking answers to Saudi complicity in the Jamal Khashoggi murder — efforts which the White House has appeared to stonewall at every turn.
Thus for now it appears “business as usual” will remain concerning the decades long US-Saudi arms pipeline.
* * *
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) further found the following other notable developments:
- Between 2009–13 and 2014–18 arms imports decreased by states in the Americas (–36 per cent), in Europe (–13 per cent), and in Africa (–6.5 per cent).
- Algeria accounted for 56 per cent of African imports of major arms in 2014–18. Most other states in Africa import very few major arms.
- The top five arms importers in sub-Saharan Africa were Nigeria, Angola, Sudan, Cameroon and Senegal. Together, they accounted for 56 per cent of arms imports to the subregion.
- Between 2009–13 and 2014–18 British arms exports increased by 5.9 per cent. In 2014–18 a total of 59 per cent of British arms exports went to the Middle East, the vast bulk of which was made up of deliveries of combat aircraft to Saudi Arabia and Oman.
- Venezuelan arms imports fell by 83 per cent between 2009–13 and 2014–18.
- China delivered major arms to 53 countries in 2014–18, compared with 41 in 2009–13 and 32 in 2004–2008. Pakistan was the main recipient (37 per cent) in 2014–18, as it has been for all five-year periods since 1991.

Comments
Post a Comment